Using the ESP8266 and the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, you can build a precise distance-sensing device.
How it Works:
The HC-SR04 works on the same principle as sonar or echolocation used by bats.
- The Trig pin sends out a high-frequency sound pulse.
The sound travels through the air, hits an object, and bounces back.
The Echo pin listens for that return signal.
By measuring the time it took for the sound to return, we can calculate the distance using the speed of sound.
1. Hardware Setup
To get started, connect your sensor to the ESP8266 according to the connection provided below:
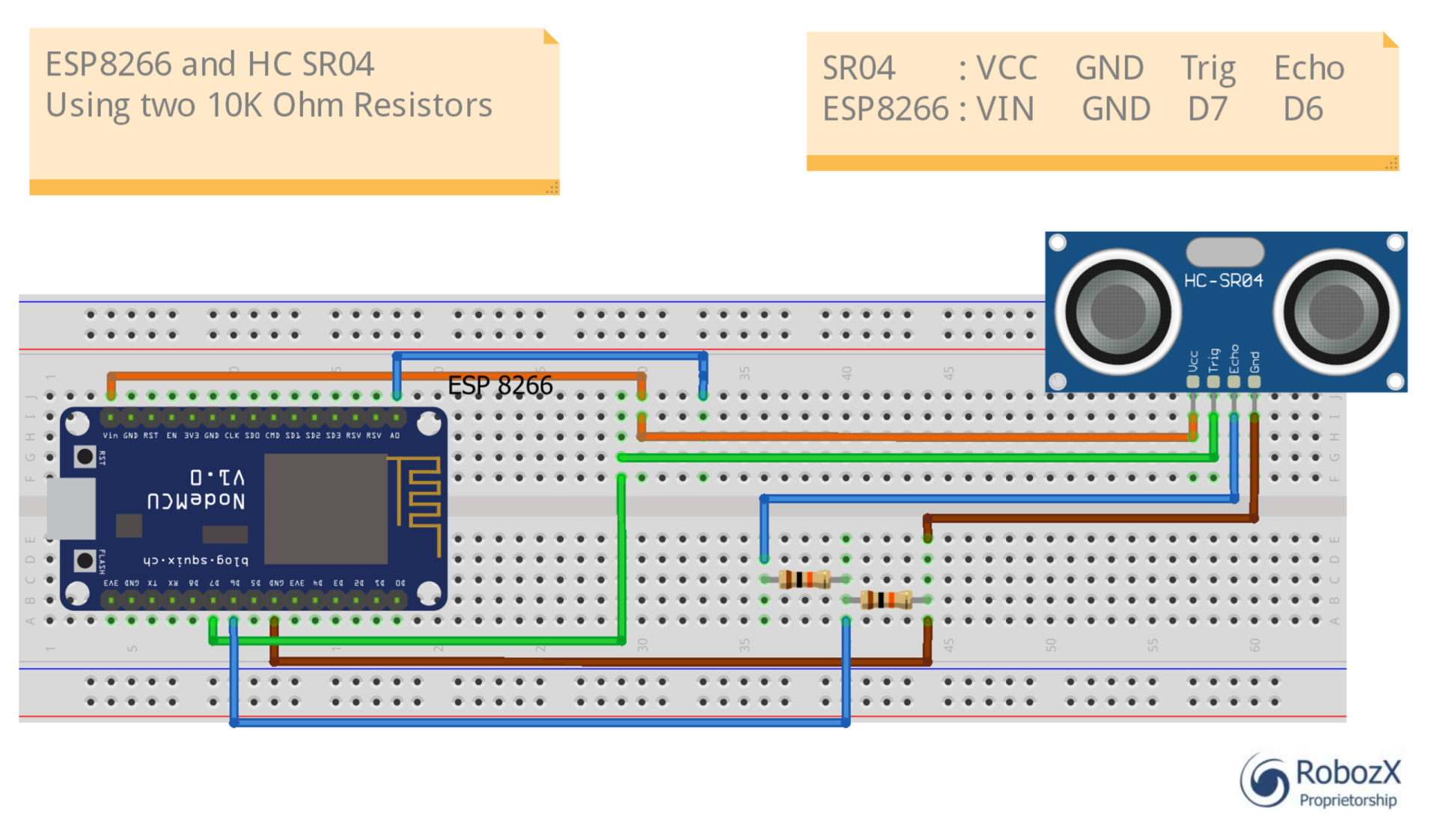
| HC-SR04 Pin | ESP8266 Pin | Purpose |
| VCC | Vin (5V) | Power (Requires 5V for best range) |
| GND | GND via 10K ohm resistor | Ground |
| Trig | D7 (GPIO 13) | Sends the pulse |
| Echo | D6 (GPIO 12) via 10K ohm resistor | Receives the pulse |
2. Understanding the Logic
We perform three main tasks in every loop:
The Trigger: It clears the
trigPinand then holds it HIGH for 10 microseconds to “fire” the ultrasonic burst.The Measurement: It uses the
pulseIn()function to measure how many microseconds theechoPinstays HIGH.The Math: Since sound travels at approximately 0.034 cm/µs, we multiply the time by 0.034. We then divide by 2 because the sound traveled to the object and back.
3. Deployment and Testing
Upload: Copy the code into your Arduino IDE and upload it to your Amica board.
Serial Monitor: Open the Serial Monitor (Tools > Serial Monitor) and set the baud rate to 9600.
Observation: Move your hand or a flat object in front of the sensor. You will see the distance in centimeters updating every 2 seconds.
/* Author: RobozX */
/* Board: ESP8266 Amica */
/* Description: Measure distance using HC-SR04 */
const int trigPin = D7; //NodeMCU D7
const int echoPin = D6; //NodeMCU D6
long duration;
int distance;
void setup() {
pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(echoPin, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2); // Delay in Microseconds
digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
// Reads the echoPin, returns the sound wave travel time in microseconds
duration = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH);
// Calculating the distance
distance= duration*0.034/2;
// Prints the distance on the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Distance: ");
Serial.println(distance);
delay(2000);
}